The importance of rfid in libraries has grown exponentially, revolutionising library management and ensuring a seamless user experience.
With RFID technology, libraries can take their operations to the next level without the need for additional resources or complicated processes.
Let’s delve into the various elements involved in implementing RFID technology in libraries and understand how it is reshapes the way libraries function.
RFID Tags:
RFID tags are small electronic devices that consist of a microprocessor chip and an antenna.
These tags are attached to every resource in the library, programmed with relevant information such as the book’s name, topic, author, and original location.
When scanned, these tags facilitate various applications involved in library management, making processes more efficient and accurate.
RFID Readers:
RFID readers are compact devices equipped with antennas that emit and receive signals from RFID tags.
They serve as the means of communication between the library’s resources and the tags attached to them.
By transferring radio signals and decoding the information from the RFID tags, these readers execute operations smoothly. Additionally, they enable real-time asset tracking and inventory management, ensuring up-to-date information.
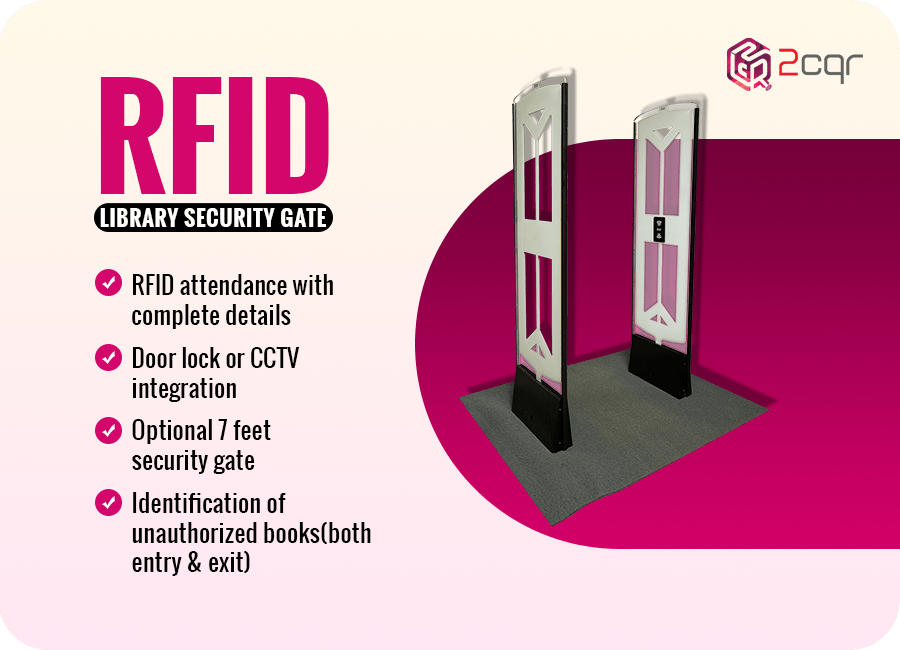
Security Gates:
Security gates, often integrated with biometric or face recognition technology, play a crucial role in enhancing library security.
These gates prevent unrecorded checkouts and protect valuable library resources from theft. They also enable the tracking of library staff attendance and ensure that the library remains updated without any difficulties.
Self-Service Kiosks:
Self-service kiosks equipped with RFID readers facilitate quick and efficient multiple checkouts.
Patrons can independently scan their borrowed items with reduced waiting times that improves the overall user experience.
Self service stations integrated with the library database, the RFID system instantly updates patron accounts, streamlining inventory management and minimizing manual resources.
Drop Boxes:
RFID drop boxes offer convenience to library users by allowing them to return books at their own convenience.
Though there are probable challenges associated with drop boxes, they will eliminate the need for library staff intervention in checking the status of overdue books, accepting returns, and updating patron accounts and the library database.
This feature greatly reduces subscriber frustration and simplifies the return process.
Intelligent Shelving:
One of the most remarkable aspects of RFID-based library management is automatic reshelving.
When users return books, RFID technology enables automatic reshelving to the original location. The data programmed in the RFID tags associated with library resources guides this process.
Intelligent shelving saves time and effort, ensuring that books are organized efficiently and allows the library staff to focus on other potential tasks.
Conclusion
Embrace the power of RFID technology in libraries to enhance user experiences and optimize library management.
By adopting RFID tags, readers, security gates, self-service kiosks, drop boxes, and intelligent shelving, libraries can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and provide a seamless experience for patrons.
Embrace this transformative technology and witness the evolution of library management into a new era.